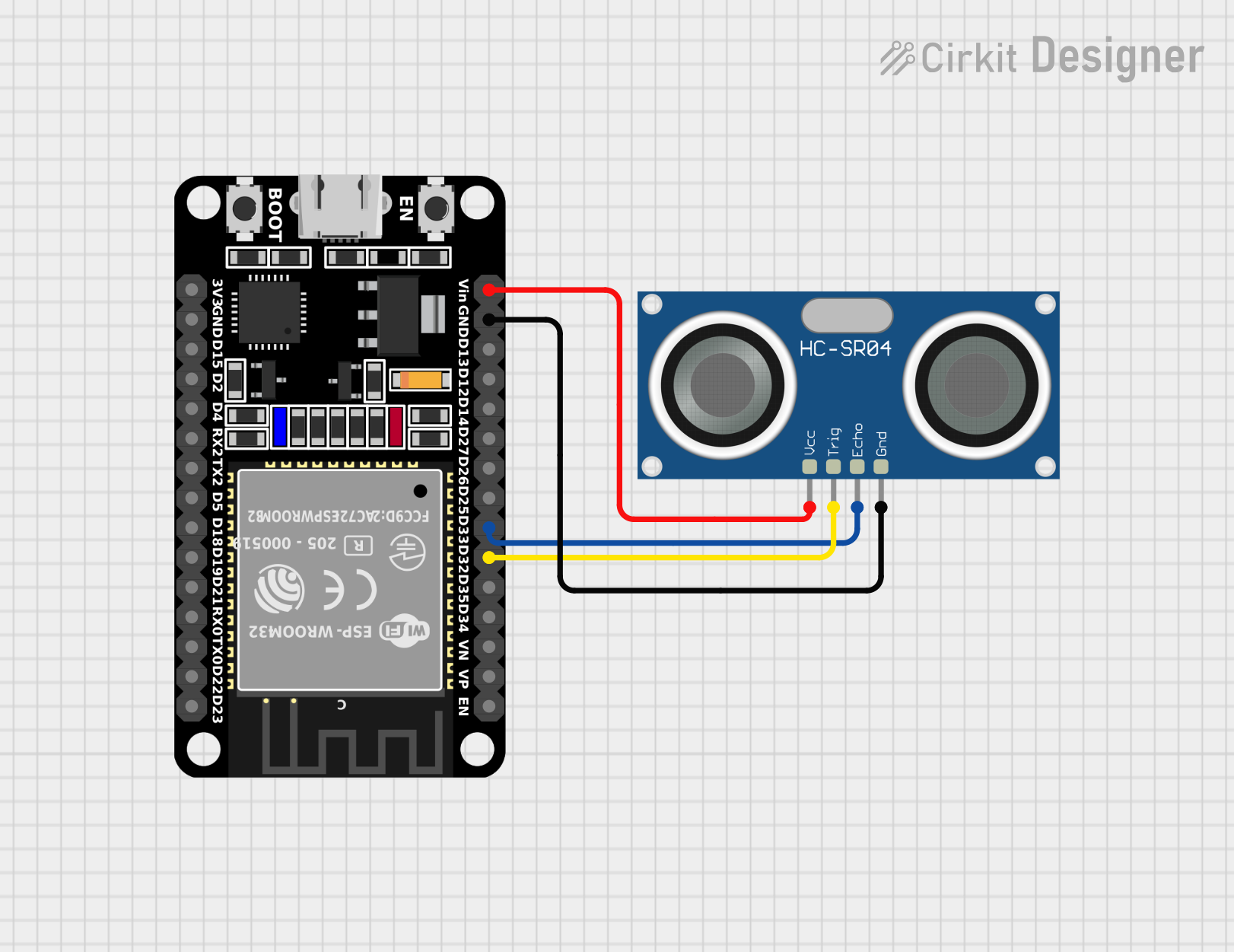
ESP32 with ultrasonic Sensor
ESP32 and NewPing library for ultrasonic distance measurements. Here’s a comprehensive guide incorporating the best aspects of previous responses and addressing potential issues:
Hardware Setup:
- ESP32: Connect the ESP32’s GPIO pins (e.g., TRIGGER and ECHO) to the corresponding pins on your ultrasonic sensor. Ensure proper wiring and power supply.
- Ultrasonic Sensor: Follow the sensor’s datasheet for specific connection instructions. Many sensors have a TRIGGER pin for sending pulses and an ECHO pin for receiving echoes.
#include <NewPing.h>
// Define sensor pins
#define TRIGGER_PIN 33
#define ECHO_PIN 34
// Maximum distance to measure (in centimeters)
#define MAX_DISTANCE 200
NewPing sonar(TRIGGER_PIN, ECHO_PIN, MAX_DISTANCE);
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
Serial.begin(115200);
}
void loop() {
// Measure distance
unsigned int distance = sonar.ping_cm();
// Print measured distance
Serial.print("Distance: ");
Serial.print(distance);
Serial.println(" cm");
// Delay for readability
delay(100);
}Explanation:
NewPing.h: This library provides functions for interacting with ultrasonic sensors.TRIGGER_PINandECHO_PIN: Replace these with the actual GPIO pins connected to your sensor.MAX_DISTANCE: Set this to the maximum distance you want to measure in centimeters.sonar.ping_cm(): This function sends a pulse to the TRIGGER pin, waits for the echo, and calculates the distance in centimeters.Serial.print()andSerial.println(): These functions are used to display the measured distance on the serial monitor.
Additional Considerations:
- Noise and Interference: Ultrasonic sensors can be susceptible to noise and interference. Consider shielding the sensor or using filtering techniques to improve accuracy.
- Environmental Factors: Factors like temperature, humidity, and obstacles can affect the accuracy of measurements. Be aware of these limitations and calibrate your sensor accordingly.
- Sensor Specifications: Refer to the sensor’s datasheet for its range, accuracy, and other specifications.
- Error Handling: Implement error handling mechanisms to deal with unexpected situations, such as sensor failures or invalid measurements.
By following these guidelines and considering the additional factors, you should be able to effectively use the ESP32 and NewPing library for ultrasonic distance measurements in your projects.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.