ESP32 Joystick Controlled Robot Using ESP-NOW Protocol & L298N Motor Driver
- 2025
🤖 ESP32 Joystick Controlled Robot Using ESP-NOW Protocol & L298N Motor Driver
Wireless bot control with speed adjustment via joystick tilt
📝 Introduction
In this project, we built a wireless robot controlled via a joystick and two ESP32 boards using the ESP-NOW communication protocol. Unlike Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, ESP-NOW enables fast, peer-to-peer data transfer between ESP32 devices using MAC addresses, making it ideal for real-time robot control.
The robot’s movement and speed are controlled through analog joystick input, and an L298N motor driver handles motor driving on the receiving end.
🔧 Hardware Used
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| 2x ESP32 | One for sending joystick data, one for receiving and controlling motors |
| Joystick Module | Outputs analog X/Y values |
| L298N Motor Driver | Dual H-Bridge to drive DC motors |
| Robot Chassis | With 2x DC motors |
| Jumper Wires + Power | Batteries or USB |
🧠 How It Works
➤ Communication Setup
- The sender ESP32 reads the X and Y analog values from a joystick.
- These values are sent via ESP-NOW protocol to the receiver ESP32.
- The receiver ESP32 processes the data and controls the L298N motor driver using the L298NX2 library.
- Speed is adjusted based on how far the joystick is pushed.
➤ Direction Mapping
- Y-axis forward → robot forward
- Y-axis backward → robot reverse
- X-axis left/right → turn accordingly
- Small movements result in low speed; full push gives max speed.
📡 Setting Up ESP-NOW Communication
To communicate using ESP-NOW, both ESP32 boards need to:
- Be in WiFi Station mode
- Share the receiver’s MAC address
- Be added as peers in the ESP-NOW network
Use this code on the receiver ESP32 to get its MAC ad
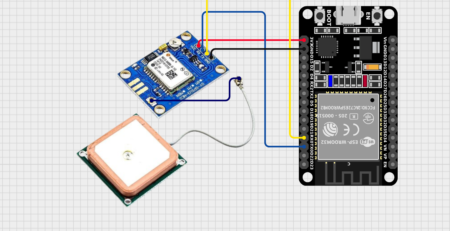
🛠️ Wiring Summary
Sender (Joystick to ESP32)
| Joystick Pin | ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
| VRx | GPIO 34 |
| VRy | GPIO 35 |
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 3.3V |
Receiver (ESP32 to L298N)
| L298N Pin | ESP32 Pin |
|---|---|
| IN1 | 18 |
| IN2 | 19 |
| IN3 | 16 |
| IN4 | 17 |
| ENA | 4 (PWM) |
| ENB | 5 (PWM) |
🎥 Demo Output
- Forward push: robot moves ahead
- Full tilt → max speed
- Side push: turns left or right
- Release joystick → bot stops
Tested delay: ~50ms for excellent real-time response
Use this code on the receiver ESP32 to get its MAC ad
/*
Rui Santos & Sara Santos – Random Nerd Tutorials
Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/get-change-esp32-esp8266-mac-address-arduino/
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files.
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#include <WiFi.h>
#include <esp_wifi.h>
void readMacAddress(){
uint8_t baseMac[6];
esp_err_t ret = esp_wifi_get_mac(WIFI_IF_STA, baseMac);
if (ret == ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x\n",
baseMac[0], baseMac[1], baseMac[2],
baseMac[3], baseMac[4], baseMac[5]);
} else {
Serial.println("Failed to read MAC address");
}
}
void setup(){
Serial.begin(115200);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
WiFi.STA.begin();
Serial.print("[DEFAULT] ESP32 Board MAC Address: ");
readMacAddress();
}
void loop(){
}
Sender Code (Joystick to ESP32)
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
const int xPin = 34; // VRx
const int yPin = 35; // VRy
const int buttonPin = 14; // SW
#define LED 2
uint8_t broadcastAddress[] = {0x30, 0xC6, 0xF7, 0x22, 0xEB, 0xD8};
typedef struct struct_message {
char a[32];
int x, y;
bool button;
} struct_message;
struct_message myData;
esp_now_peer_info_t peerInfo;
bool isConnected = false;
unsigned long lastSendTime = 0;
unsigned long timeoutDuration = 2000; // 2 seconds timeout
void OnDataSent(const uint8_t *mac_addr, esp_now_send_status_t status) {
if (status == ESP_NOW_SEND_SUCCESS) {
isConnected = true;
lastSendTime = millis(); // reset timeout
Serial.println("✅ Delivery Success");
} else {
Serial.println("❌ Delivery Fail");
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(buttonPin, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_register_send_cb(OnDataSent);
memcpy(peerInfo.peer_addr, broadcastAddress, 6);
peerInfo.channel = 0;
peerInfo.encrypt = false;
if (esp_now_add_peer(&peerInfo) != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Failed to add peer");
return;
}
}
void loop() {
int xValue = analogRead(xPin);
int yValue = analogRead(yPin);
bool buttonPressed = digitalRead(buttonPin) == LOW;
int mappedX = map(xValue, 0, 4095, 0, 100);
int mappedY = map(yValue, 0, 4095, 0, 100);
myData.x = mappedX;
myData.y = mappedY;
myData.button = buttonPressed;
strcpy(myData.a, "Joystick Data");
esp_err_t result = esp_now_send(broadcastAddress, (uint8_t *) &myData, sizeof(myData));
if (result == ESP_OK) {
Serial.printf("📤 Sent: X=%d, Y=%d, Btn=%s\n", mappedX, mappedY, buttonPressed ? "Pressed" : "Released");
} else {
Serial.println("🚫 Error sending the data");
}
// ⚠️ Simulate connection timeout (if no successful sends recently)
if (millis() - lastSendTime > timeoutDuration) {
isConnected = false;
}
digitalWrite(LED, isConnected ? HIGH : LOW);
delay(200);
}
Receiver Code (Joystick to ESP32)
#include <L298NX2.h>
#include <esp_now.h>
#include <WiFi.h>
// Motor pins
#define ENA 4
#define IN_1 16
#define IN_2 17
#define ENB 5
#define IN_3 18
#define IN_4 19
#define LED 2
#define TIMEOUT 5000
L298NX2 mybot(ENA, IN_1, IN_2, ENB, IN_3, IN_4);
typedef struct struct_message {
char a[32];
int x, y;
bool button;
} struct_message;
struct_message myData;
unsigned long lastRecvTime = 0;
void OnDataRecv(const uint8_t * mac, const uint8_t *incomingData, int len) {
memcpy(&myData, incomingData, sizeof(myData));
Serial.print("Message: "); Serial.println(myData.a);
Serial.print("Xaxis: "); Serial.println(myData.x);
Serial.print("Yaxis: "); Serial.println(myData.y);
Serial.print("Button: "); Serial.println(myData.button ? "Pressed" : "Released");
Serial.println();
digitalWrite(LED, HIGH);
lastRecvTime = millis();
// Basic Joystick-based Movement
if (myData.y == 0 && myData.x!=0) {
mybot.forward();
Serial.println("Forward");
}
else if (myData.y==100 && myData.x!=100) {
mybot.backward();
Serial.println("Backward");
}
else if (myData.x==0 && myData.y!=0) {
mybot.forwardA();
mybot.backwardB();
Serial.println("Left");
}
else if (myData.x==100 && myData.y!=100) {
mybot.forwardB();
mybot.backwardA();
Serial.println("Right");
}
else {
mybot.stop();
Serial.println("Stop");
}
}
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
pinMode(LED, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA);
if (esp_now_init() != ESP_OK) {
Serial.println("Error initializing ESP-NOW");
return;
}
esp_now_register_recv_cb(esp_now_recv_cb_t(OnDataRecv));
mybot.setSpeed(100);
mybot.stop(); // Ensure motors are off on start
}
void loop() {
if (millis() - lastRecvTime > TIMEOUT) {
digitalWrite(LED, LOW);
mybot.stop(); // stop bot if no data received
}
}





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.